Gandhi: A Biography
First Online: August 15, 1997
Page Last Updated: December 07, 2024
First See: Introduction to learn Who was Gandhi?
Early Years of Gandhi
Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi (1869-1948), also known as Mahatma Gandhi, was born in Porbandar in the present day state of Gujarat in India on October 2, 1869. He was raised in a very conservative family that had affiliations with the ruling family of Kathiawad. He was educated in schools of Rajkot and was married at the age of 13. Then he studied law at University College in London. In 1891, after having been admitted to the British bar, Gandhi returned to India and attempted to establish a law practice in Bomaby, without much success. Two years later, an Indian firm with interests in South Africa retained him as legal adviser in a lawsuit in its office in Durban. Arriving in Durban, Gandhi found himself treated as a member of an inferior race. He was appalled at the widespread denial of civil liberties and political rights to Indian immigrants to South Africa. He threw himself into the struggle for elementary rights for Indians.
See Also: Parentage and Childhood from Gandhi's autobiography
Resistance to Injustice
Gandhi remained in South Africa for twenty years, suffering imprisonment many times. In 1896, after being attacked and humiliated by white South Africans, Gandhi began to teach a policy of passive resistance to, and non-cooperation with, the South African authorities. Part of the inspiration for this policy came from the Russian writer Leo Tolstoy, whose influence on Gandhi was profound. Gandhi also acknowledged his debt to the teachings of Christ and to the 19th-century American writer Henry David Thoreau, especially to Thoreau's famous essay "Civil Disobedience." Gandhi considered the terms passive resistance and civil disobedience inadequate for his purposes, however, and coined another term, Satyagraha (from Sanskrit, "truth and firmness"). During the Boer War, Gandhi organized an ambulance corps for the British army and commanded a Red Cross unit. After the war he returned to his campaign for Indian rights. In 1910, he founded Tolstoy Farm, near Durban, a cooperative colony for Indians. In 1914 the government of the Union of South Africa made important concessions to Gandhi's demands, including recognition of Indian marriages and abolition of the poll tax for them. His work in South Africa complete, he returned to India.
![]()
Campaign for Home Rule
 Gandhi became a leader in a complex struggle, the
Indian campaign for home
rule. Following World War I, in which he played an active part in recruiting campaigns,
Gandhi, again advocating Satyagraha, launched his movement of
non-violent resistance to Great
Britain. When, in 1919, Parliament passed the Rowlatt Acts, giving the Indian colonial
authorities emergency powers to deal with so-called revolutionary activities, Satyagraha
spread throughout India, gaining millions of followers. A demonstration against the
Rowlatt Acts resulted in a massacre of Indians at Amritsar by British soldiers; in 1920, when the
British government failed to make amends, Gandhi proclaimed an organized campaign of
non-cooperation. Indians in public office resigned, government agencies such as courts of
law were boycotted, and Indian children were withdrawn from government schools. Throughout
India, streets were blocked by squatting Indians who refused to rise even when beaten by
police. Gandhi was arrested, but the British were soon forced to release him.
Gandhi became a leader in a complex struggle, the
Indian campaign for home
rule. Following World War I, in which he played an active part in recruiting campaigns,
Gandhi, again advocating Satyagraha, launched his movement of
non-violent resistance to Great
Britain. When, in 1919, Parliament passed the Rowlatt Acts, giving the Indian colonial
authorities emergency powers to deal with so-called revolutionary activities, Satyagraha
spread throughout India, gaining millions of followers. A demonstration against the
Rowlatt Acts resulted in a massacre of Indians at Amritsar by British soldiers; in 1920, when the
British government failed to make amends, Gandhi proclaimed an organized campaign of
non-cooperation. Indians in public office resigned, government agencies such as courts of
law were boycotted, and Indian children were withdrawn from government schools. Throughout
India, streets were blocked by squatting Indians who refused to rise even when beaten by
police. Gandhi was arrested, but the British were soon forced to release him.
Economic independence for India, involving the complete boycott of British goods, was made
a corollary of Gandhi's Swaraj (from Sanskrit, "self-governing") movement. The economic
aspects of the movement were significant, for the exploitation of Indian villagers by
British industrialists had resulted in extreme poverty in the country and the virtual
destruction of Indian home industries. As a remedy for such poverty, Gandhi advocated
revival of cottage industries; he began to use a spinning wheel as a token of the return
to the simple village life he preached, and of the renewal of native Indian industries.
Gandhi became the international symbol of a free India. He lived a spiritual and ascetic
life of prayer, fasting, and meditation. His union with his wife became, as he himself
stated, that of a brother and sister. Refusing earthly possessions, he wore the loincloth
and shawl of the lowliest Indian and subsisted on vegetables, fruit juices, and goat's
milk. Indians revered him as a saint and began to call him Mahatma (great-souled), a title
reserved for the greatest sages. Gandhi's advocacy of nonviolence, known as ahimsa
(non-violence), was the expression of a way of life implicit in the Hindu religion. By the
Indian practice of nonviolence, Gandhi held, Great Britain too would eventually consider
violence useless and would leave India.
The Mahatma's political and spiritual hold on India was so great that the British
authorities dared not interfere with him. In 1921 the Indian National
Congress, the group
that spearheaded the movement for nationhood, gave Gandhi complete executive authority,
with the right of naming his own successor. The Indian population, however, could not
fully comprehend the unworldly ahimsa. A series of armed revolts against the
British
broke out, culminating in such violence that Gandhi confessed the failure of the
civil-disobedience campaign he had called, and ended it. The British government again
seized and imprisoned him in 1922.
After his release from prison in 1924, Gandhi withdrew from active politics and devoted
himself to propagating communal unity. Unavoidably, however, he was again drawn into the
vortex of the struggle for independence. In 1930 the Mahatma proclaimed a new campaign of
civil disobedience, calling upon the Indian population to refuse to pay taxes,
particularly the tax on salt. The campaign was a march to the sea, in which thousands of
Indians followed Gandhi from Ahmedabad to the Arabian Sea, where they made salt by
evaporating sea water. Once more the Indian leader was arrested, but he was released in
1931, halting the campaign after the British made concessions to his demands. In the same
year Gandhi represented the Indian National Congress at a conference in London.
V.N. O'key/Kamat's Potpourri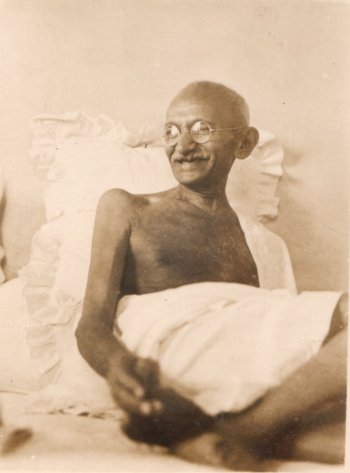
Smiling Gandhi
Photograph by V.N. O'key, circa 1945
Gandhi takes on Domestic Problems
In 1932, Gandhi began new civil-disobedience campaigns
against the British. Arrested twice, the Mahatma fasted for long periods several times;
these fasts were effective measures against the British, because revolution might well
have broken out in India if he had died. In September 1932, while in jail, Gandhi
undertook a "fast unto death" to improve the status of the Hindu Untouchables.
The British, by permitting the Untouchables to be considered as a separate part of the
Indian electorate, were, according to Gandhi, countenancing an injustice. Although he was
himself a member of an upper caste, Gandhi was the great leader of the
movement in India dedicated to eradicating the unjust social and economic aspects of the
caste system.
In 1934 Gandhi formally resigned from politics, being replaced as leader of the Congress
party by Jawaharlal Nehru. Gandhi traveled through India, teaching ahimsa and demanding
eradication of "untouchability." The esteem in which he was held was the measure
of his political power. So great was this power that the limited home rule granted by the
British in 1935 could not be implemented until Gandhi approved it. A few years later, in
1939, he again returned to active political life because of the pending federation of
Indian principalities with the rest of India. His first act was a fast, designed to force
the ruler of the state of Rajkot to modify his autocratic rule. Public unrest caused by
the fast was so great that the colonial government intervened; the demands were granted.
The Mahatma again became the most important political figure in India.
© K. L. Kamat

Man of Firm Step
![]()
Independence for India
When World War II broke out, the Congress party and Gandhi demanded a declaration of war aims and their application to India. As a reaction to the unsatisfactory response from the British, the party decided not to support Britain in the war unless the country were granted complete and immediate independence. The British refused, offering compromises that were rejected. When Japan entered the war, Gandhi still refused to agree to Indian participation. He was interned in 1942 but was released two years later because of failing health.Times of India/Kamat's Potpourri
Men Carrying Gandhi, Noakhali
By 1944 the Indian struggle for independence was in its final stages, the British
government having agreed to independence on condition that the two contending nationalist
groups, the Muslim League and the Congress party, should resolve their differences. Gandhi
stood steadfastly against the partition of India but ultimately had to agree, in the hope
that internal peace would be achieved after the Muslim demand for separation had been
satisfied. India and Pakistan became separate states when the British granted India its
independence in 1947 (see: Tryst with
Destiny -- the story of India's independence). During the riots that followed the partition of India, Gandhi
pleaded with Hindus and Muslims to live together peacefully. Riots engulfed Calcutta, one
of the largest cities in India, and the Mahatma fasted until disturbances ceased. On
January 13, 1948, he undertook another successful fast in New Delhi to bring about peace,
but on January 30, 12 days after the termination of that fast, as he was on his way to his
evening prayer meeting, he was assassinated by a fanatic Hindu.
Gandhi's death was regarded as an international catastrophe. His place in humanity was
measured not in terms of the 20th century, but in terms of history. A period of mourning
was set aside in the United Nations General Assembly, and condolences to India were
expressed by all countries. Religious violence soon waned in India and Pakistan, and the
teachings of Gandhi came to inspire nonviolent movements elsewhere, notably in the U.S.A.
under the civil rights leader Martin Luther King, Jr. and in South Africa under Nelson
Mandela.
See Also:
- Sardar Bhagat Singh
- Bal Gangadhar Tilak
- Indian War of Independence
- Gandhiji and his views on Women
- India's Struggle for Freedom
![]()
References
- "Gandhi, Mohandas Karamchand," Microsoft (R) Encarta. Copyright � 1993 Microsoft Corporation. Copyright � 1993 Funk & Wagnall's Corporation
- Green Martin (Ed) Gandhi in India, 1987
- A compilation of research papers on Gandhi for further study
� The Creative works are copyrighted by respective photographers, artists
and writers.
Most of Gandhi's Writings � by Navajivan Trust. Check with us
before you reproduce.